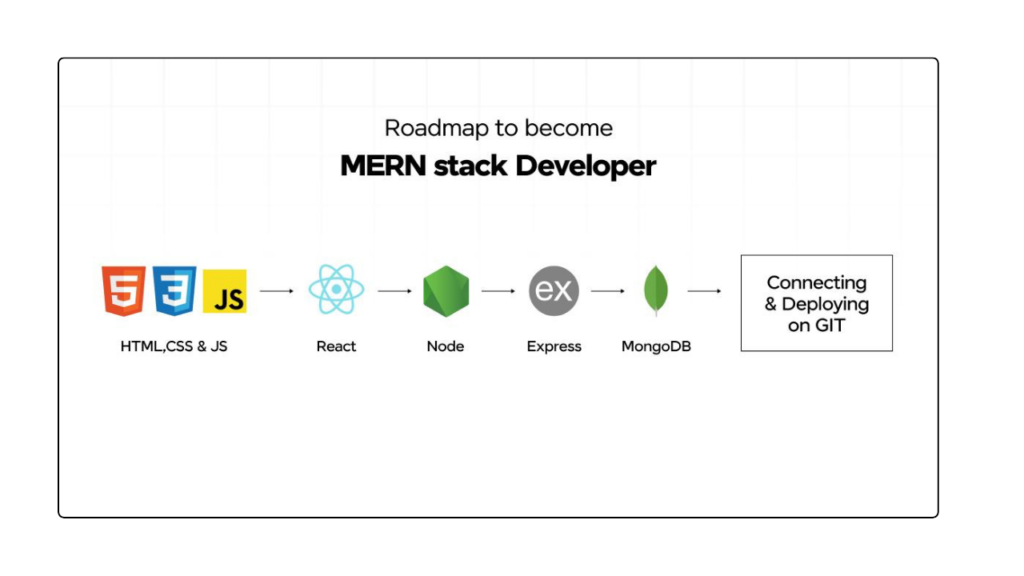
Discover the 2024 MERN Stack Developer Roadmap and become proficient in MongoDB, Express, React, and Node.js to begin your full-stack journey.

What is the MERN Stack Learning Path?
MERN Stack is a full-stack framework. This includes:
-
- MongoDB – A NoSQL database for storing data.
-
- Express.js – A web application framework for Node.js, handling backend logic and API routing.
-
- React – A front-end library for building user interfaces and handling client-side logic.
-
- Node.js – A runtime environment for running JavaScript on the server side, allowing you to build an application’s backend.
Why is it used?
Full stack development encompasses both frontend and backend development. The front end is what users interact with directly in their browser, including elements like buttons, input boxes, and overall design. This code is executed on the user’s device, making it visible to them and necessary for rendering the user interface. On the other hand, the backend handles the logic and functionality that users don’t see, such as processing requests, managing databases, and delivering responses. This code runs on servers in data centers, managing operations like query processing and data manipulation that support the functionality of the front end.
In web development, the MERN stack is a popular full-stack framework that integrates four key technologies: MongoDB, Express.js, React, and Node.js. MongoDB is a NoSQL database used for storing data, Express.js is a backend framework for building web applications and APIs, React is a frontend library for creating dynamic user interfaces, and Node.js is a runtime environment for executing JavaScript on the server side. Together, these technologies provide a comprehensive solution for building web applications, covering both the client and server sides.
Where is it used?
The MERN stack is used in various scenarios, particularly when a cohesive, JavaScript-based development environment is desired. It is ideal for building single-page applications (SPAs) where React’s component-based architecture offers a dynamic user experience and Node.js ensures efficient server-side processing. This stack is also suitable for applications requiring real-time data updates and seamless integration between the front end and back end. By utilizing a single language across the entire stack, development can be more streamlined and cohesive.
Moreover, the MERN stack is effective for projects that need robust data management and fast, scalable performance. MongoDB’s flexible schema design fits well with applications that require rapid changes to data structures, while Node.js’s non-blocking architecture supports high-performance, real-time applications. Express.js facilitates the development of RESTful APIs, and React provides a responsive user interface, making the MERN stack a versatile choice for modern web development needs.
How do I get started with the MERN Stack Career Path?
What to learn in React.js?
1. Components
2. JSX
3. Props
4. State
5. Lifecycle Methods
6. Hooks (useState, useEffect, etc.)
7. Context API
8. React Router
9. Redux (or other state management libraries)
10. Event Handling
11. Forms and Form Handling
12. Refs
13. Higher-Order Components (HOCs)
14. Render Props
15. Error Boundaries
16. Portals
17. Custom Hooks
18. React Performance Optimization
19. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) with Next.js
20. Testing with React Testing Library and Jest
What to learn in MongoDB?
1. Documents and Collections
2. BSON (Binary JSON)
3. CRUD Operations
4. Schema Design
5. Indexing
6. Aggregation Framework
7. MongoDB Query Language (MQL)
8. Data Modeling
9. Replication
10. Sharding
11. Transactions
12. MongoDB Atlas
13. GridFS
14. MongoDB Compass
15. Mongoose (ODM for Node.js)
16. MongoDB Security (Authentication, Authorization, Encryption)
17. Backup and Restore
18. Performance Tuning
19. MongoDB Change Streams
20. Time Series Collections
What to learn in Nodejs?
1. Core Modules (fs, http, path, etc.)
2. Asynchronous Programming (Callbacks, Promises, Async/Await)
3. Event-Driven Architecture
4. Express.js (Web Framework)
5. Middleware
6. Routing
7. Error Handling
8. RESTful API Design
9. Database Integration (MongoDB, SQL, etc.)
10. Authentication and Authorization
11. File Upload and Handling
12. Environment Variables and Configuration
13. Logging
14. Unit Testing and Integration Testing
15. Security Practices (e.g., OWASP Top Ten)
16. Performance Optimization
17. Deployment (e.g., PM2, Docker)
18. WebSockets and Real-Time Communication
19. Caching (e.g., Redis)
20. Server-side rendering (SSR) with frameworks like Next.js
What to learn in Express?
1. Basic Concepts and Setup
2. Routing
3. Middleware
4. Request and Response Objects
5. Error Handling
6. Static File Serving
7. Template Engines (e.g., Pug, EJS, Handlebars)
8. Query Parameters and URL Parameters
9. Form Data Handling
10. Sessions and Cookies
11. Authentication and Authorization
12. RESTful API Design
13. File Upload and Handling
14. Database Integration
15. Security Practices (e.g., Helmet, CORS)
16. Logging and Debugging
17. Performance Optimization
18. Deployment (e.g., PM2, Docker)
19. Testing (e.g., Mocha, Chai, Supertest)
20. Integrating Third-Party Services